You’ve likely seen the “4K” sticker on new televisions, computer monitors, and even smartphones. It’s a term that has become synonymous with high-quality, crystal-clear visuals. But what does 4K resolution actually mean? It’s more than just a marketing buzzword; it represents a significant leap forward in display technology that has reshaped our viewing experiences, from watching movies to playing video games.
Understanding 4K involves diving into the world of pixels, aspect ratios, and industry standards. This technology offers four times the detail of the once-dominant Full HD, providing a sharper, more immersive picture. This guide will demystify 4K resolution, exploring its technical details, the tangible benefits it brings to your screen, and how it compares to other resolutions. We will cover everything you need to know about this popular display standard.
What Does 4K Actually Mean?
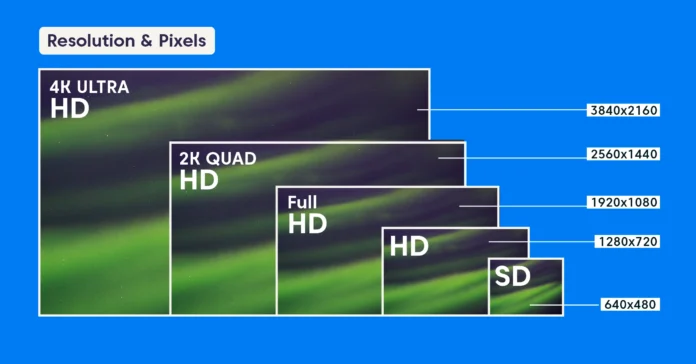
At its core, 4K resolution refers to a display with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000 pixels. Pixels are the tiny dots of light that combine to create the image you see on a screen. The more pixels packed into a display, the higher the resolution, which results in a sharper and more detailed picture.
While the term “4K” is used broadly, it actually encompasses two primary standards:
- 4K UHD (Ultra High Definition): This is the standard you’ll find in most consumer televisions and monitors. It has a resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels. If you do the math, that’s 8,294,400 pixels in total. This resolution has a 16:9 aspect ratio, which is the standard widescreen format for TVs, online streaming content, and most computer monitors. It’s called Ultra High Definition because it offers exactly four times the number of pixels as 1080p Full HD (1920 x 1080), with twice the horizontal and twice the vertical pixel count.
- DCI 4K (Digital Cinema Initiatives): This standard is used in the professional film and digital cinema industry. DCI 4K has a slightly wider resolution of 4096 x 2160 pixels. This results in a slightly wider aspect ratio than 16:9, which is common for theatrical movie screenings. While some high-end consumer projectors and monitors support DCI 4K, the vast majority of “4K” devices you’ll encounter are 4K UHD.
For the average consumer, the terms “4K,” “4K UHD,” and “Ultra HD” are used interchangeably to refer to the 3840 x 2160 resolution. This has become the new benchmark for high-quality home entertainment.
The Technical Side of 4K
To fully appreciate what 4K brings to the table, it helps to understand a few key technical specifications that work alongside the pixel count to deliver a superior image.
Pixel Density and Its Importance
4K TVs have four times more pixels than traditional Full HD (1920 x 1080) TVs. This increased pixel density is what makes the picture so much more vivid and detailed. On a large screen, this difference is dramatic. For instance, on a 65-inch TV, a 4K display has much smaller, more densely packed pixels than a 1080p TV of the same size.
This higher density means you can sit closer to the screen without seeing the individual pixels that make up the image. The picture remains sharp and clear, creating a more immersive, cinema-like experience in your living room.
Refresh Rate (Hz)
The refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates how many times per second the image on the screen is updated. A higher refresh rate results in smoother motion, which is especially important for fast-paced content like sports and video games. Standard 4K TVs typically offer a 60Hz refresh rate, which is sufficient for most movies and TV shows. However, many premium models now feature a 120Hz native refresh rate, providing exceptional motion clarity and reducing blur during fast action sequences.
High Dynamic Range (HDR)
While 4K resolution gives you more pixels, High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology gives you better pixels. HDR expands the range of both color and contrast, allowing for brighter whites, deeper blacks, and a wider spectrum of colors. This creates a much more vibrant, realistic, and lifelike image.
Common HDR formats include:
- HDR10: The open standard and most common form of HDR.
- Dolby Vision: A premium, dynamic HDR format that optimizes the picture scene by scene.
- HDR10+: An open-standard dynamic format that competes with Dolby Vision.
- HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma): Primarily used for broadcast television.
A 4K display paired with HDR technology is the key to unlocking the best possible picture quality available today.
Color Depth (Bit Depth)
Color depth determines how many different shades of color a display can produce. Most standard displays use 8-bit color, which allows for 16.7 million colors. Many 4K HDR displays, however, support 10-bit color. This increases the number of possible colors to over one billion, resulting in smoother color gradations and eliminating the “banding” effect that can sometimes appear in scenes with subtle color shifts, like a sunset.
The Benefits of 4K Resolution
Upgrading to 4K isn’t just about having the latest tech; it provides tangible benefits that enhance your viewing experience in several ways.
Unmatched Detail and Clarity
The most significant advantage of 4K is the incredible level of detail. With four times the pixels of 1080p, images are rendered with stunning sharpness and realism. You can see finer textures in clothing, individual leaves on a tree, and subtle details in distant backgrounds that would be lost on a lower-resolution screen. This clarity makes for a more engaging and lifelike picture.
Better Viewing on Large Screens
The benefits of 4K become more apparent as screen size increases. On a large TV (65 inches and above), the higher pixel density of 4K is crucial for maintaining a sharp image. On a 1080p TV of the same size, the pixels are larger and more spread out, which can make the image appear soft or pixelated, especially when viewed up close. With 4K, the picture remains crisp and detailed, even on a massive screen.
More Immersive Viewing Experience
The combination of high pixel density and the ability to sit closer to the screen without losing quality creates a more immersive field of view. Your screen can fill more of your vision, pulling you into the action much like a movie theater screen does. This deeper sense of immersion is a game-changer for movies, documentaries, and video games.
The Power of Upscaling
What if the content you’re watching isn’t in 4K? This is where upscaling comes in. Modern 4K TVs are equipped with powerful processors that intelligently enhance lower-resolution content (like 720p, 1080p, or even standard definition) to look better on a 4K screen.
Upscaling isn’t just stretching the image. The TV’s processor analyzes the picture, reduces noise, sharpens edges, and enhances details to make the content look as close to native 4K quality as possible. This means your existing Blu-ray collection and broadcast TV shows will look better than ever on a 4K display.
Comparing 4K to Other Resolutions
To put 4K in context, let’s see how it stacks up against other common resolutions.
4K vs. Full HD (1080p)
- Resolution: 4K (3840 x 2160) has four times the pixels of Full HD (1920 x 1080).
- Clarity: The difference is most noticeable on larger screens and when sitting closer. 4K provides a significantly sharper, more detailed image.
- Content: While 1080p content is still widespread, 4K content is now the standard for streaming services, modern video games, and UHD Blu-rays.
- Verdict: 4K is the clear winner and the current industry standard. It offers a major upgrade in picture quality over 1080p, especially for home theater setups.
4K vs. 8K
- Resolution: 8K (7680 x 4320) has four times the pixels of 4K and sixteen times the pixels of 1080p.
- Clarity: 8K offers an incredible level of detail, but the difference between 4K and 8K is much harder for the human eye to perceive on typical screen sizes from normal viewing distances. You would need a very large screen (80 inches or more) and to sit very close to truly appreciate the difference.
- Content: Native 8K content is extremely limited. Most of what you watch on an 8K TV will be upscaled 4K content.
- Verdict: For most people, 4K is the sweet spot. It provides a fantastic picture with plenty of available content. 8K is a future-facing technology, but for now, 4K offers a better balance of performance, content availability, and price.
Applications of 4K Technology
4K is no longer a niche technology. It has been widely adopted across various fields, changing how we consume and create visual media.
Home Entertainment
This is the most common application of 4K. Streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, Amazon Prime Video, and Apple TV+ offer vast libraries of movies and TV shows in 4K, often with HDR. Ultra HD Blu-ray discs provide the best possible 4K picture and sound quality for physical media collectors. Major sporting events are also increasingly being broadcast and streamed in 4K, offering fans an unparalleled view of the action.
Gaming
4K has revolutionized the gaming world. Modern consoles like the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X are designed to output games in stunning 4K resolution at smooth frame rates. On PC, powerful graphics cards can drive even higher frame rates for an incredibly fluid and detailed gaming experience. The sharpness and detail of 4K allow gamers to spot enemies from further away and become more immersed in expansive digital worlds.
Professional Use
In the professional realm, 4K is essential.
- Filmmaking: Directors and cinematographers shoot in 4K (or higher) to capture the maximum amount of detail and have more flexibility in post-production for tasks like cropping, stabilizing, and visual effects.
- Graphic Design and Photography: 4K monitors provide designers and photographers with a highly detailed canvas, allowing them to see their work with exceptional clarity and color accuracy.
- Medical Imaging: In medicine, 4K displays are used to view detailed medical scans, helping doctors make more accurate diagnoses.
Content Creation
The rise of affordable 4K cameras, including those on smartphones, has democratized high-quality video production. YouTubers, vloggers, and independent filmmakers can now produce professional-looking content in 4K. Even if the final video is delivered in 1080p, shooting in 4K provides a higher-quality source image that results in a sharper final product.
Is It Worth Upgrading to 4K?
Absolutely. If you are in the market for a new TV or monitor, choosing a 4K model is a wise investment. Prices for 4K displays have become very competitive, and the amount of available 4K content is growing every day. The improvement in picture quality, especially when combined with HDR, is a significant step up from older standards.
For anyone who enjoys movies, TV shows, or gaming, a 4K display offers a more immersive, detailed, and visually satisfying experience. It has firmly established itself as the new standard for visual entertainment, and its benefits are clear to see.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Do I need special cables for 4K?
A: To ensure you get the best 4K signal, especially with HDR and higher refresh rates (60Hz and above), it’s recommended to use a High-Speed or Ultra High-Speed HDMI cable (often labeled as HDMI 2.0 or 2.1 compatible). Older HDMI cables may not have enough bandwidth to support the full capabilities of 4K.
Q: What internet speed do I need for 4K streaming?
A: Most streaming services, like Netflix, recommend a stable internet connection of at least 15-25 Mbps for a smooth 4K streaming experience. Faster is always better, especially if other devices are using your network at the same time.
Q: Is all 4K content the same quality?
A: No. The quality of 4K content can vary. A movie on a UHD Blu-ray disc will typically have a higher bitrate (more data per second) and therefore better picture quality than the same movie streamed in 4K. Streaming services use compression to save bandwidth, which can sometimes result in a slightly less detailed image compared to physical media.
Q: Can I use a 4K TV as a computer monitor?
A: Yes, you can. Many people use 4K TVs as large computer monitors. They offer a huge amount of screen real estate for multitasking. However, for tasks that require reading a lot of text, some users may find that a dedicated computer monitor with features designed for close-up viewing is more comfortable.
Q: Is 4K the same as Dolby Vision?
A: No, they are different but complementary technologies. 4K refers to the resolution (the number of pixels). Dolby Vision is an advanced type of HDR (High Dynamic Range) that enhances the color, contrast, and brightness of those pixels. A display can be 4K without having Dolby Vision, but the best viewing experience comes from a 4K display that also supports Dolby Vision.
Q: Will I notice the difference with 4K on a smaller screen?
A: The difference is less pronounced on smaller screens (under 40 inches) from a normal viewing distance. However, even on smaller screens, 4K can provide a sharper image, especially for text and fine details. On devices like laptops and smartphones, where you hold the screen close to your face, the higher pixel density of a 4K display can be very noticeable.